Medical billing vs revenue cycle management is a crucial topic in the healthcare industry that often goes unnoticed but plays a vital role in ensuring financial stability. It’s essential to understand how these two processes, while interconnected, serve distinct functions within healthcare organizations.
Medical billing primarily focuses on the billing and collection of payments for healthcare services, ensuring that providers are compensated for their services rendered. On the other hand, revenue cycle management encompasses a broader scope, including the entire financial process from patient registration to the final payment, aiming to optimize overall revenue through effective management of the revenue cycle.
Understanding Medical Billing
Medical billing is a crucial aspect of the healthcare industry, focusing on the process of translating healthcare services rendered into a financial transaction. It ensures that healthcare providers are reimbursed for their services, making it an essential component of the revenue cycle. Understanding medical billing helps streamline operations, reduce errors, and improve cash flow for medical practices.The medical billing process involves several key steps, starting with patient registration and continuing through the submission of claims to insurance companies.
The significance of this process cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the financial health of healthcare providers. Efficient medical billing practices contribute to timely payments, increased revenue, and better patient satisfaction.
Process of Medical Billing
The medical billing process consists of multiple stages, each with its significance in ensuring accurate and prompt reimbursement. Below are the main components involved in medical billing:
- Patient Registration: The initial step involves collecting patient information, including demographics, insurance details, and medical history.
- Charge Capture: This stage includes documenting all services provided during a patient visit, ensuring everything is recorded accurately for billing purposes.
- Claim Submission: Claims are prepared using standardized codes (CPT, ICD-10) and submitted to insurance providers for reimbursement.
- Payment Posting: Once payments are received, they are posted to the patient’s accounts, and any adjustments or denials are reviewed and addressed.
- Accounts Receivable Follow-Up: This involves tracking outstanding claims and following up with payers to ensure timely payments, as well as addressing any discrepancies.
Types of Services Included in Medical Billing
Medical billing covers a wide array of services associated with a patient’s healthcare experience. These services are essential for accurate billing and can include:
- Consultations: Charges for physician consultations, evaluations, and diagnostic services.
- Procedures: Billing for surgical and non-surgical procedures performed by healthcare professionals.
- Diagnostic Testing: Charges related to laboratory tests, radiology, and imaging services.
- Follow-Up Visits: Costs associated with subsequent patient visits for ongoing care or treatment adjustments.
- Preventive Services: Billing for services such as vaccinations and routine physical exams that promote health and prevent illness.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Medical Biller
A medical biller plays a vital role in the healthcare revenue cycle, ensuring that all billing processes are executed efficiently. Responsibilities include:
- Insurance Verification: Confirming patient insurance eligibility and coverage before services are rendered.
- Claim Preparation: Accurately coding and preparing claims to submit to insurance companies based on provided medical documentation.
- Denial Management: Analyzing and resolving denied claims through appeals or resubmissions, ensuring maximum reimbursement.
- Patient Billing: Generating patient statements for any balance due after insurance payments, including clear explanations of charges.
- Reporting: Generating financial reports and metrics to help healthcare organizations monitor their billing performance and cash flow.
Accurate medical billing not only ensures timely reimbursement but also contributes significantly to the overall financial stability of healthcare practices.
Overview of Revenue Cycle Management
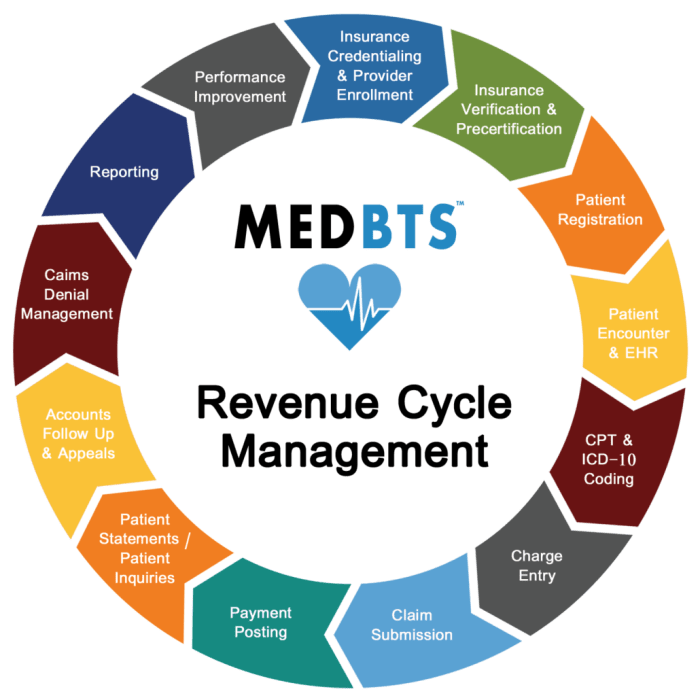
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) is a critical process that encompasses all the administrative and clinical functions that contribute to the capture, management, and collection of patient service revenue in healthcare settings. It covers the entire patient journey, from the initial appointment scheduling to the final payment of the billed services. RCM is essential for ensuring that healthcare organizations maintain a healthy cash flow and profitability while delivering quality care.RCM involves multiple components that work together to optimize the financial aspects of healthcare services.
It includes patient registration, insurance verification, charge capture, coding, billing, collections, and account reconciliation. Each of these components plays a distinct role in managing revenue streams, ensuring compliance with regulations, and minimizing errors that can lead to revenue loss. The efficiency of RCM can significantly impact the overall financial health of a healthcare provider.
Components of Revenue Cycle Management
Understanding the components of RCM helps in distinguishing it from medical billing, as RCM is broader and encompasses more than just the billing process. Key components include:
- Patient Registration: Collecting patient information and insurance details at the start of the patient journey.
- Insurance Verification: Confirming the patient’s insurance coverage and benefits before services are provided.
- Charge Capture: Recording the services provided to patients accurately to ensure proper billing.
- Coding: Translating medical diagnoses and procedures into standardized codes for billing purposes.
- Billing: Generating invoices and sending them to patients and payers for the services rendered.
- Collections: Following up on unpaid invoices and managing accounts receivable.
- Account Reconciliation: Ensuring that payments received match the billed amounts and resolving discrepancies.
Each of these components plays a vital role in the workflow of RCM. While medical billing focuses on the billing and payment aspect, RCM encompasses broader processes to ensure that all financial transactions related to patient care are efficiently managed.
Key Metrics for Assessing Revenue Cycle Management
Evaluating the effectiveness of RCM involves tracking specific key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect its efficiency and effectiveness. These metrics provide insights into areas of improvement and help in decision-making processes. Important metrics include:
- Days in Accounts Receivable (AR): The average number of days it takes to collect payment after a service is delivered. A lower number indicates better performance.
- Claim Denial Rate: The percentage of claims that are denied by payers upon submission. A high denial rate may indicate issues in coding or documentation.
- Net Collection Rate: The percentage of collectible revenue that is actually collected. This metric helps assess the effectiveness of collections processes.
- Charges per Encounter: The average amount billed per patient visit or service. This can indicate the complexity and volume of services provided.
- Patient Satisfaction Scores: Feedback from patients regarding their billing experience can influence overall revenue and payment behaviors.
Tracking these metrics allows healthcare organizations to pinpoint areas for improvement and develop strategies to enhance their revenue cycle processes.
Differences Between Medical Billing and Revenue Cycle Management

Medical billing and revenue cycle management (RCM) are crucial components of healthcare finance, each serving distinct yet interrelated purposes. Understanding their differences not only aids healthcare providers in optimizing their operations but also supports financial sustainability in an increasingly complex healthcare landscape. While both processes aim to manage the financial aspects of patient care, they do so with varying goals and methodologies.
Goals and Objectives of Medical Billing and Revenue Cycle Management
The primary goal of medical billing is to ensure that healthcare providers receive timely and accurate payment for services rendered. This entails coding medical services, submitting claims to insurance companies, and following up on unpaid claims. In contrast, revenue cycle management encompasses a broader scope, focusing on the entire patient financial experience from pre-visit to post-service. RCM aims to optimize revenue capture, improve patient satisfaction, and streamline operational efficiencies across the healthcare continuum.
- Medical Billing: Focuses on the billing process, ensuring accurate claim submissions and payments.
- Revenue Cycle Management: Encompasses all financial aspects, including patient registration, insurance verification, billing, and collections.
Technological Tools in Medical Billing and Revenue Cycle Management
Technological advancements play a significant role in both medical billing and RCM, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in financial processes. Various tools and software applications are integral to these functions.
- Medical Billing Software: Specifically designed for the billing process, these tools help automate claim submissions and track payments, reducing errors and speeding up collections.
- RCM Platforms: Comprehensive systems that integrate various functions, including patient scheduling, coding, billing, and analytics. These platforms provide real-time data insights to help optimize revenue cycle performance.
The benefits of these technologies include improved accuracy in billing, reduced claim denials, and enhanced visibility into the financial health of a healthcare organization. For example, an RCM platform can identify trends in claim denials, enabling proactive measures to address common issues before they escalate.
Impact on Hospital Finances
Effective medical billing and revenue cycle management have a direct impact on a hospital’s financial health. Streamlined billing processes and optimized revenue cycles contribute to better cash flow, reduced days in accounts receivable, and overall financial stability.
- Improved Cash Flow: Efficient billing and RCM processes minimize delays in payment, thus enhancing cash flow. Hospitals can maintain operations and invest in necessary resources.
- Reduction in Claim Denials: By ensuring accurate coding and timely submissions, hospitals can significantly reduce the number of denied claims, leading to increased revenue.
- Enhanced Patient Satisfaction: A smooth financial experience contributes to patient satisfaction, which can influence return visits and patient referrals.
In summary, while medical billing and revenue cycle management both aim to secure payment for services, they differ in their scope, objectives, and the technologies employed. Understanding these differences is essential for healthcare organizations aiming to improve their financial performance and patient experiences.
Final Summary

In summary, distinguishing between medical billing and revenue cycle management allows healthcare professionals to better understand their roles in enhancing financial performance. Both processes are essential; effective medical billing ensures accurate payments, while robust revenue cycle management streamlines the entire process, ultimately contributing to the healthcare provider’s success.
Top FAQs
What is the main difference between medical billing and revenue cycle management?
Medical billing focuses on the billing process for services rendered, while revenue cycle management encompasses the entire financial process from patient registration to final payment.
What role does technology play in medical billing and revenue cycle management?
Technology enhances efficiency and accuracy in both processes, automating billing tasks and improving data management for better financial oversight.
How can effective medical billing impact a healthcare provider’s revenue?
Effective medical billing ensures timely and accurate payments, reducing denials and improving cash flow for healthcare providers.
What are some key performance indicators for revenue cycle management?
Common KPIs include days in accounts receivable, claim denial rates, and net collection rates, which help assess the efficiency of the revenue cycle.
Why is training important for medical billers?
Training ensures that medical billers are knowledgeable about coding, regulations, and billing processes, which reduces errors and improves revenue collection.





